## The VIPER Mission Canceled: A Lunar Dream Deferred
NASA’s $450 million lunar ice-mapping mission, known as VIPER (Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover), has been canceled due to cost overruns and schedule setbacks. This mission aimed to unearth the Moon’s water ice deposits, crucial for future human colonies and interstellar wayposts. Let’s delve into the reasons behind this cancellation and its implications for future lunar exploration.
# Introduction
NASA’s $450 million lunar ice-mapping mission, known as VIPER (Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover), has been canceled due to cost overruns and schedule setbacks. This mission aimed to unearth the Moon’s water ice deposits, crucial for future human colonies and interstellar wayposts. Let’s delve into the reasons behind this cancellation and its implications for future lunar exploration.
# VIPER: A Bold Stride Towards Lunar Resources
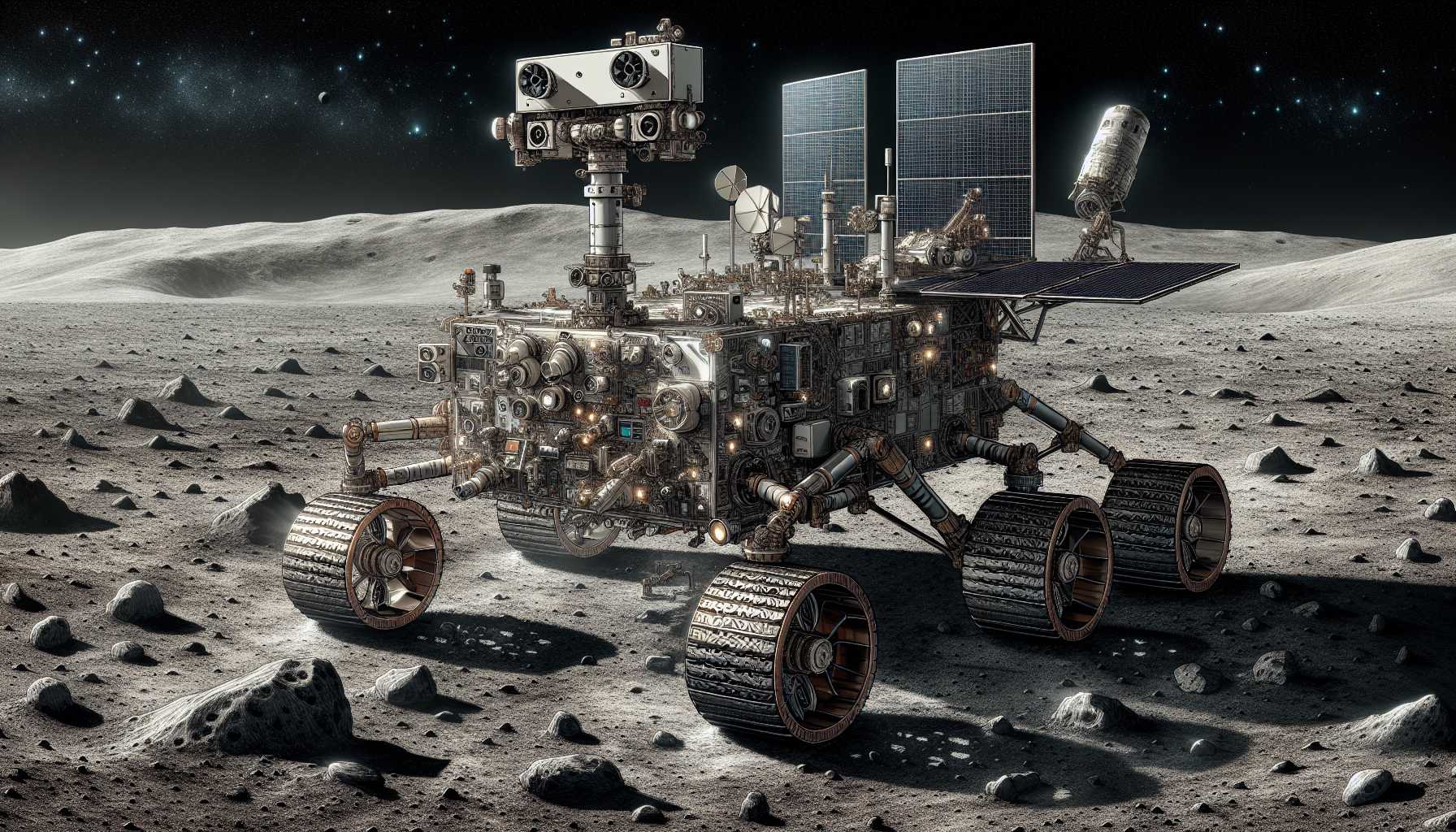
VIPER, a four-wheeled rover, was designed to scout for ice in the Moon’s permanently shadowed south pole regions. This mission represented a significant step towards understanding lunar resources, vital for establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon.
# Technical Hurdles and Strategic Setbacks
Navigating the ice-laden terrain of the Moon’s permanently shadowed regions presented significant technical challenges. The solar-powered rover required meticulous planning to operate in near-real time from Earth while maneuvering through unknown lunar soil conditions. Additionally, cost overruns and project delays pushed the mission’s launch date from late 2023 to 2025.
# NASA’s Strategic Shift
NASA’s decision to cancel VIPER reflects a strategic shift towards prioritizing other commercial lunar payload initiatives. While $450 million has already been spent, NASA will salvage components for future missions, preserving critical research and development investments.
# The Bigger Picture: NASA’s Artemis and Beyond
VIPER was an integral part of NASA’s Artemis program, designed to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Despite its cancellation, NASA remains committed to exploring lunar resources with missions like the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1), scheduled for a 2024 landing.
# A Glimpse into the Fusion Future: Powering Tomorrow’s World
While NASA tackles the complexities of the lunar frontier, the race for nuclear fusion, the process that powers the sun, continues on Earth. Fusion holds the promise of nearly infinite clean energy, and the industry has seen an influx of over $900 million in investments.
# Fusion Trailblazers: Helion and Zap’s Progress
Fusion pioneers Helion Energy and Zap Energy are making significant strides. Helion is nearing the operational phase of its seventh-generation prototype device, Polaris, while Zap Energy’s new Century device has reached plasma temperatures of 11 to 37 million degrees Celsius.
# Is Fusion the Clean Energy Grail?
Fusion energy is lauded as the holy grail of clean energy due to its lack of radioactive waste concerns. However, significant financial support and technological breakthroughs are still needed for commercial viability.
# Conclusion: The Journey Continues
The cancellation of VIPER is a reminder of the challenges in space exploration. However, it also highlights NASA’s adaptability and commitment to its long-term goals. Similarly, the strides in fusion energy underscore the relentless quest for breakthrough innovations. The future holds immense possibilities as NASA redirects its lunar aspirations and fusion technology edges closer to transforming our energy paradigm. Stay tuned to this thrilling journey as we continue to document the saga of humanity’s relentless search for the ultimate frontiers of technology and exploration.
# Images
# SEO Optimization
* **Title:** The VIPER Mission Canceled: A Lunar Dream Deferred
* **Meta Description:** NASA’s VIPER mission to explore lunar ice deposits has been canceled. Learn about the reasons behind this decision and the future of lunar exploration.
* **Keywords:** VIPER mission, lunar ice, NASA, Artemis program, fusion energy, Helion Energy, Zap Energy, clean energy
* **Headings:** Use H2 and H3 headings to structure the content and improve readability.
* **Images:** Use alt tags to describe the images for accessibility and SEO.
* **Internal Linking:** Link to relevant articles on your website to improve user engagement and SEO.